Medical Die Casting & Precision Manufacturing for Healthcare OEMs
IEC Mould is a precision die casting and machining manufacturer supporting global medical device OEMs with high-performance aluminum, magnesium, and zinc components. We work closely with engineering, procurement, and quality teams from early feasibility and DFM evaluation through tooling, mass production, CNC machining, finishing, and assembly.
Medical devices demand high dimensional accuracy, lightweight construction, corrosion resistance, consistent finishes, and reliable documentation support—capabilities IEC Mould delivers through controlled manufacturing processes and strict quality management systems certified to ISO 9001 and IATF 16949.

Why Medical Devices Need Metal Casting Components

Medical devices and surgical equipment require compact, lightweight, durable, and corrosion-resistant metal components that can withstand continuous use, cleaning cycles, and environmental exposure.
For these reasons, aluminum and zinc die casting has become a preferred process for producing housings, frames, brackets, and structural elements used in diagnostic equipment, monitoring systems, surgical instruments, and portable medical devices.
Compared with plastics or stamped metal, die-cast medical parts offer:
- Higher structural rigidity
- Improved dimensional stability
- Superior heat dissipation
- Better shielding against EMI/RFI
- Longer component lifespan
- High-volume consistency with lower unit cost
Die casting enables medical device manufacturers to combine functional performance with compact exterior design—critical for modern portable, digital, and handheld medical systems.
Engineering Challenges & Medical Industry Pain Points
Medical device OEMs and contract manufacturers typically face the following engineering and regulatory challenges during product development and mass production:
| Pain Point | Impact on Medical Device Production | Engineering Solution from IEC |
|---|---|---|
| Tight tolerances for assembly | Misalignment, leakage, vibration, poor sealing, non-conforming assemblies | DFM tolerance prediction + precision HPDC + multi-axis CNC finishing ensures stable fits down to ±0.01 mm |
| Complex housing geometries | Higher tooling cost, machining time, and reject rates | Moldflow-driven tooling + optimized gate/runner/venting + multi-slide inserts reduce complexity and machining dependency |
| EMI/RFI shielding requirements | Signal distortion, reduced sensor accuracy, failed certification | Aluminum die casting + conductive surface finishing + controlled wall thickness improves shielding effectiveness |
| Lightweight & compact design | Structural integrity + thermal dissipation trade-offs | Material selection + ribbing + topology-informed HPDC design improves stiffness-to-weight ratio |
| Cosmetic surface requirements | Increased rejection during final QC | Integrated finishing stack (brushing, blasting, coating, anodizing) delivers Class-A cosmetic surfaces |
| Quality & traceability compliance | Higher documentation and regulatory burden | ISO 9001 QMS + full traceability + PPAP + CPK data + 3D CMM reports reduce compliance risks |
How We Solve These Pain Points for Medical Casting Parts
IEC’s medical die casting solutions are built to support both development speed and compliance-critical manufacturing, including:
Early DFM for Medical Metal Parts
Scope: Early manufacturability & tolerance planning
Key Engineering Actions:
- Wall thickness optimization (shielding vs weight trade-offs)
- Ribbing, bosses & datum structure for rigidity
- Undercut & deep cavity moldability review
- CNC allowance & datum reference planning
Outcome: Fewer late-stage tooling modifications & faster validation cycles
Moldflow & Tooling Integration
Scope: Tooling accuracy & porosity control
Key Engineering Actions:
- Gate and runner design for balanced flow
- Venting path design to reduce gas traps
- Thermal balance for dimensional stability
- Ejection & cooling layout for cycle stability
Outcome: Improved yield, better surface integrity, reduced porosity — critical for medical housings
Die Casting + CNC Hybrid Manufacturing
Scope: Net-shape + precision finishing
Capabilities:
- High pressure die casting (HPDC) for structural housings
- 3-axis, 4-axis, 5-axis CNC for precision interfaces
- Controlled datum features & sealing surfaces
Outcome: CNC used only where needed, reducing cost without compromising precision
Finishing & Cosmetic Control Stack
Scope: Surface quality & durability consistency
Processes:
- Bead blasting
- Brushing
- Powder coating
- Liquid painting
- Anodizing (Aluminum)
- Conductive finishing (optional)
Outcome: Achieves consumer-grade cosmetics + medical-grade durability simultaneously
Quality, Inspection & Documentation
Scope: Regulatory compliance & traceability readiness
Provided Deliverables:
- 3D CMM dimensional reports
- Material test certifications (Incoming & outgoing)
- PPAP, FAI, CP, PFMEA, Control Plan
- RoHS / REACH compliance statements
Outcome: Supports medical OEM audits & compliance documentation with confidence
Low-variance Mass Production Control
Scope: Scaling from prototype to stable series runs
Manufacturing Control Measures:
- SPC (Statistical Process Control)
- APQP for tooling + process intro
- CPK capability tracking for key dimensions
- Lot traceability with serialization options
- Preventive maintenance on dies & CNC
- COSMETIC AQL sampling for visible housings
Outcome:Stable long-term supply with minimized variability & reject rates
Metal Die Casting Material Options for Medical Device Components
Material selection affects strength, mass, biocompatibility, cost, corrosion resistance, and manufacturability. We support multiple materials for medical parts:
Aluminum Alloys Die Casting
Aluminum is widely used in housings, frameworks, and diagnostic devices requiring EMI shielding. Common alloys for die casting or machining include:
- ADC12 / A380 (excellent castability)
- A360 (better corrosion resistance)
- 6061 / 6063 (machined or extrusion-grade)
- AlSi10Mg series (low porosity for structural parts)
Advantages:
- Lightweight with good strength
- Corrosion resistant
- Good machining performance
- Compatible with anodizing
- Non-magnetic (MRI-friendly)


Magnesium Alloys Die Casting
Common alloy:
- AZ91D
Advantages:
- 30–35% lighter than aluminum
- High specific strength
- Good damping characteristics (useful for handheld devices)
Used for surgical handheld instruments and portable devices.
Zinc Alloys Die Casting
Common alloys, commonly used in dental tools, knobs, ergonomic interfaces, and mechanical linkages.
- Zamak 3 / Zamak 5
Advantages:
- Excellent dimensional accuracy
- Thin-wall capability
- Superior surface finish for cosmetic parts
- Ideal for complex small components and mechanisms

Common Medical Components Manufactured by Die Casting & CNC
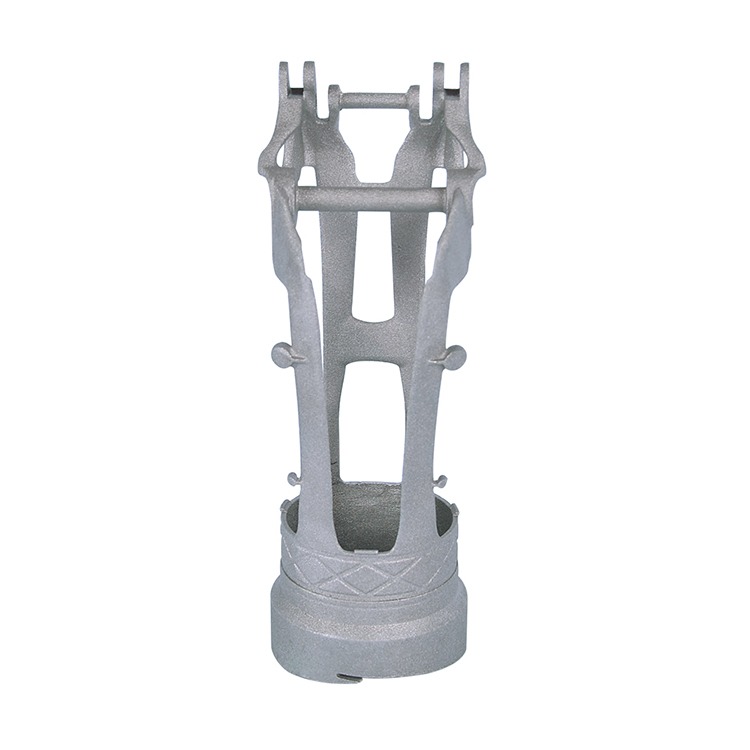
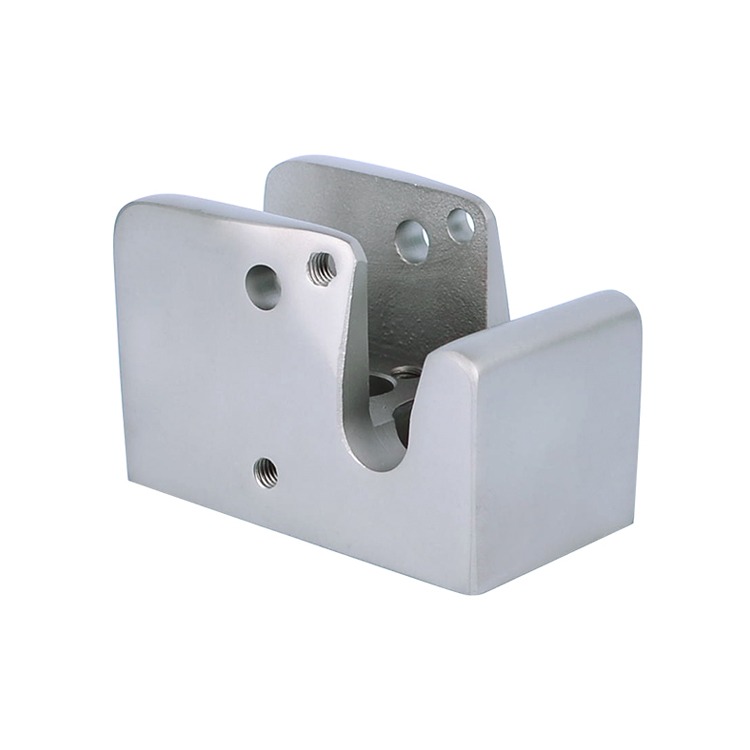
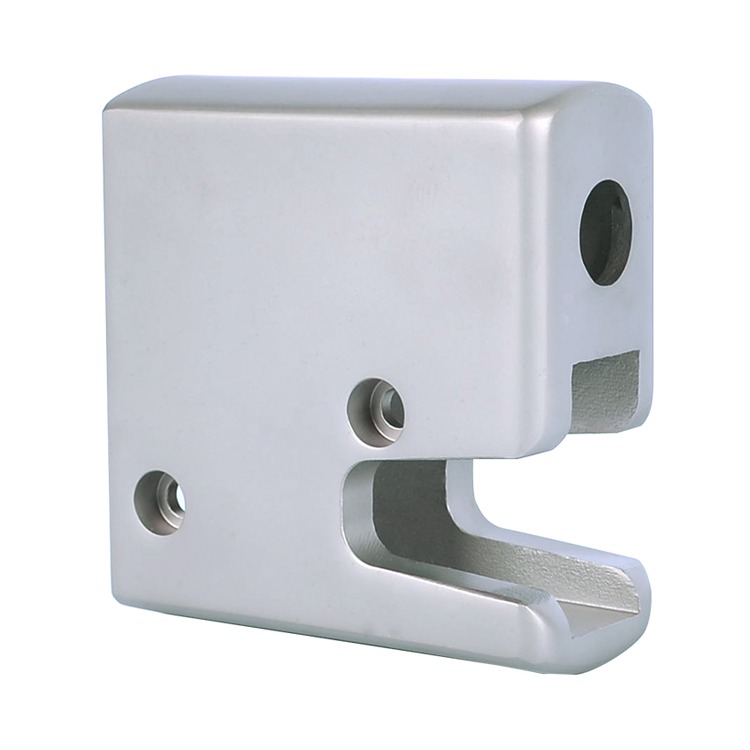
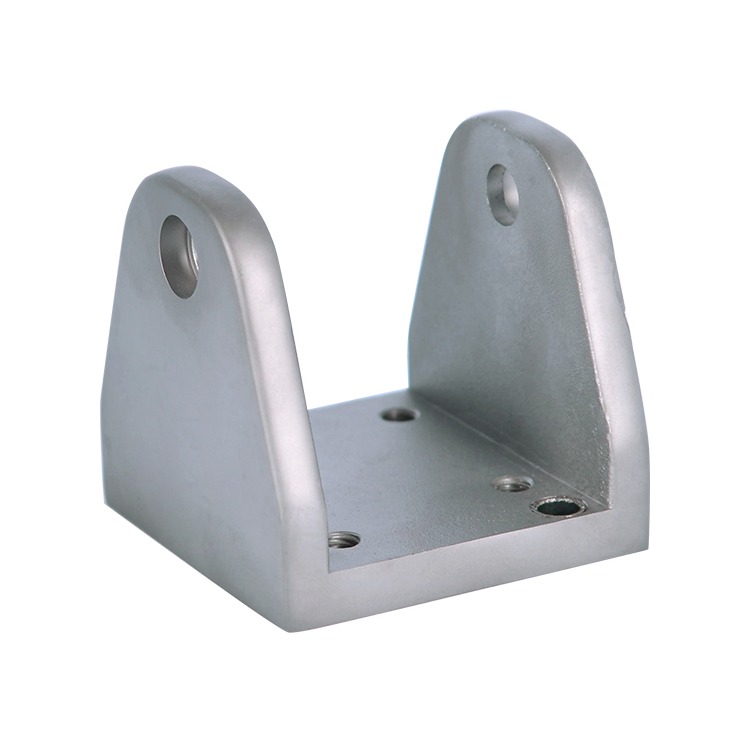
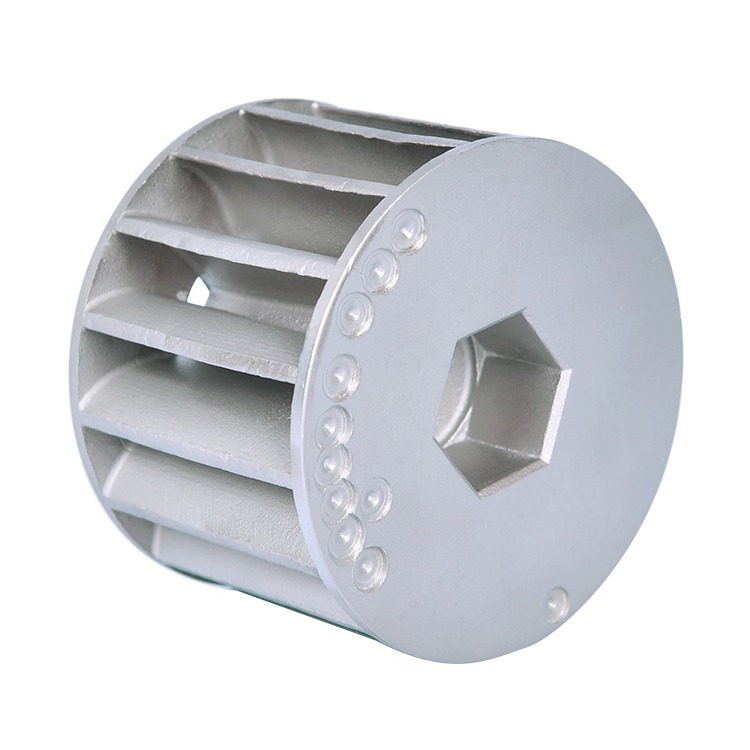
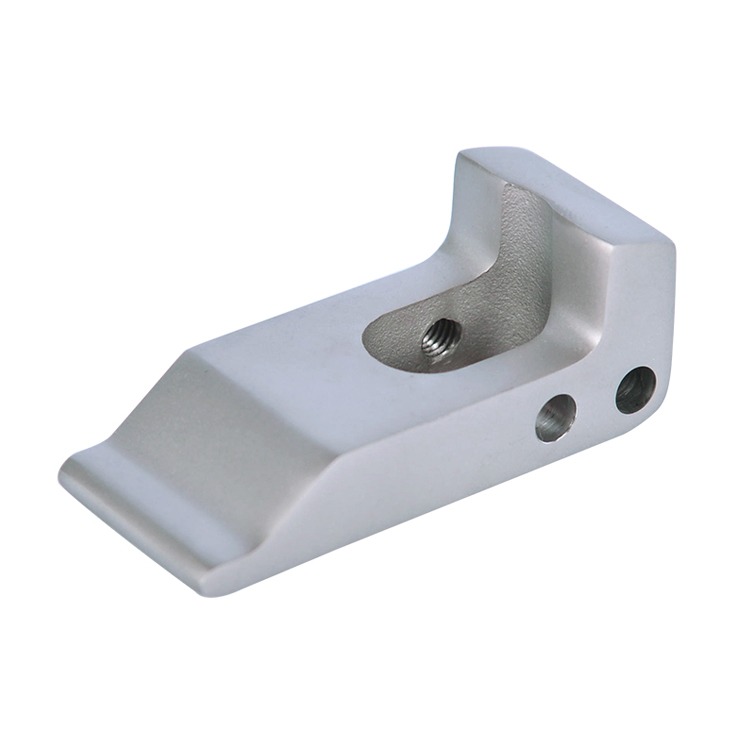






We supply die cast and machined components for a wide range of medical applications, including:
Surgical & Operating Room Equipment
- Surgical instrument housings
- Adjustable mechanism brackets
- Surgical lighting system components
- Tool handles and ergonomic grips
- Sterilization tray metal fixtures
Healthcare Electronics & Monitoring Devices
- Patient monitor housings
- PCB mounting frames
- ECG/EEG equipment enclosures
- Power module heat-sink components
- Battery & charger housings
Rehabilitation & Patient Mobility Devices
- Wheelchair and mobility hardware
- Mechanical adjustment joints
- Structural supports and frames
- Custom mounting and interface parts
Hospital Hardware & Infrastructure
- Bed mechanisms and control housings
- Medical cart frames and brackets
- Pump and valve components
- Industrial-grade connectors
Diagnostic and Imaging Equipment
- MRI and CT structural brackets
- Ultrasound device aluminum housings
- X-ray detector frames
- Sensor mounting fixtures
- RF shielding enclosures
Dental Devices & Dental Lab Equipment
- Dental chair structural components
- Handpiece housings and sleeves
- Dental imaging brackets
- Polishing & suction system housings
These product categories often require repeatable long-term manufacturing, material compliance, and revision-controlled documentation — areas where IEC Mould maintains strong capability.
Engineering DFM & Moldflow Support for Medical Components
Medical components often involve thin walls, functional geometries, and aesthetic expectations. Early collaboration reduces cost and prevents engineering failures. Our DFM engineering support includes:
Geometry Feasibility Review
We evaluate:
- Draft angles
- Undercuts
- Thin walls
- Bosses and ribs
- Sharp corners or transitions
- Gating and venting paths
Moldflow & Simulation
Simulation detects:
- Fill imbalance
- Cold shuts
- Air entrapment
- Weld lines
- Porosity concentration
- Hot spots and shrinkage
Assembly & Integration Support
We ensure compatibility with:
- Plastic housings
- Bearings & shafts
- Sensors & electronics
- O-ring grooves & sealing paths
Design-to-Cost Optimization
We propose changes that reduce:
- Cycle time
- Material usage
- Secondary machining
- Tool complexity
Tooling & Die Casting Manufacturing Process for Medical Devices
IEC Mould integrates tooling, die casting, machining, finishing, assembly, and inspection into a coherent manufacturing process suitable for long-term production.
Standard Manufacturing Workflow
- RFQ & drawing review
- DFM & feasibility confirmation
- Moldflow analysis
- Tooling design
- Tool steel selection & fabrication
- Mold trials
- Dimensional inspection
- HPDC mass production
- CNC machining & tapping
- Deburring & cleaning
- Surface finishing
- Final inspection & FAI reports
- Packaging & documentation
- Batch traceability & shipment
Tooling Capabilities
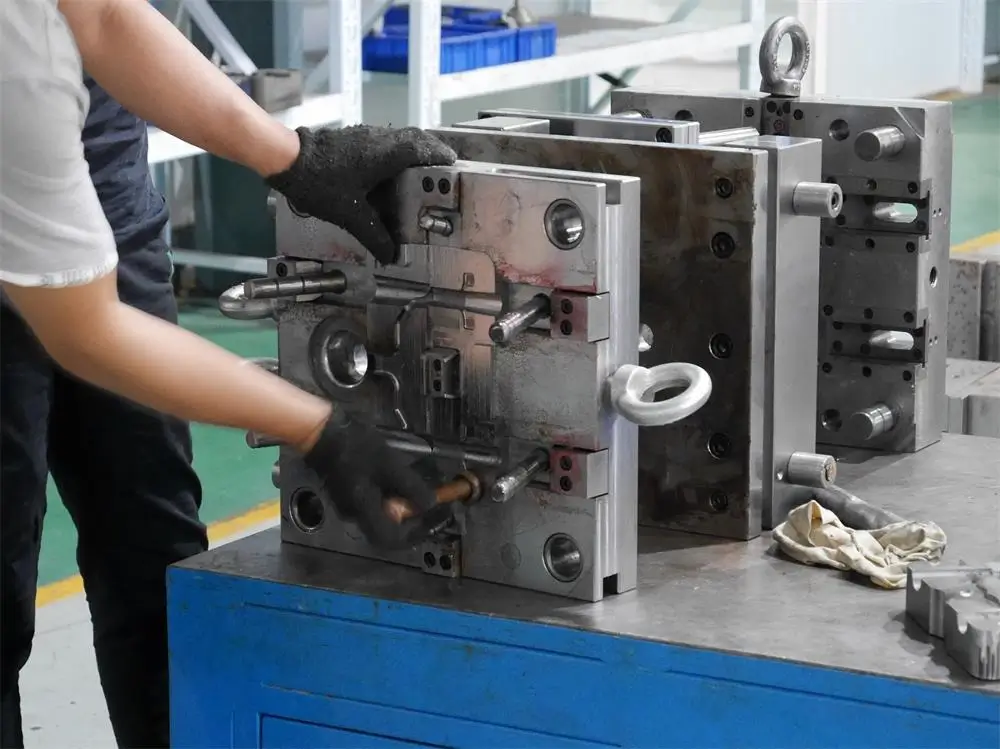

- Multi-slide tooling
- Thin-wall tooling
- Hot runner & vacuum venting
- Rapid cooling circuits
- Cavity pressure monitoring (when required)
- EDM, high-speed milling, and precision grinding
Die Casting Capabilities
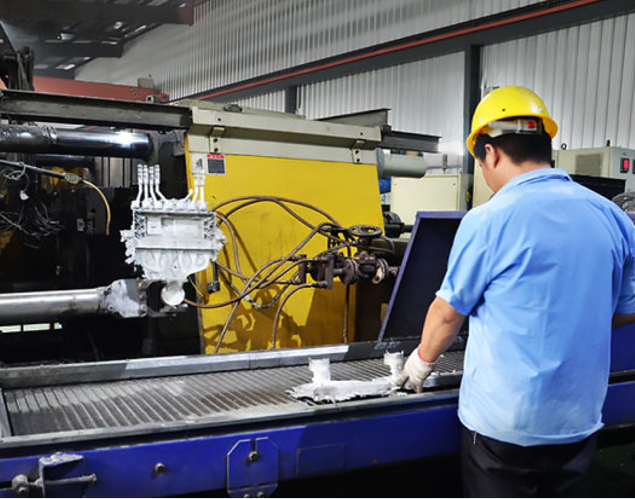

- HPDC from 80T to 1250T
- Vacuum assist for porosity reduction
- Water-cooling for dimensional stability
- Process control via temperature & shot monitoring
Secondary Operations
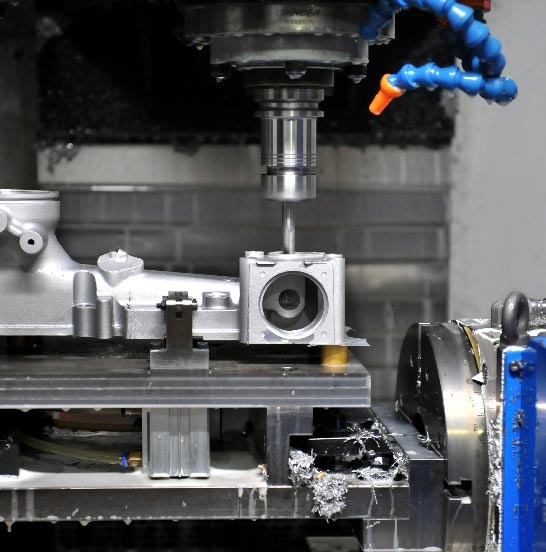
- CNC machining (3/4/5-axis)
- Turning
- Threading (M, UNC/UNF, MJ)
- Reaming & tapping
- Deburring & polishing
- Helicoil insert installation
CNC Machining for Medical Components
CNC machining enhances precision for features that are not achievable by casting alone.
Machining Capabilities
- 3-axis, 4-axis, and 5-axis milling
- Swiss-type turning for small shafts & pins
- Micro-hole drilling
- Tapping and threading
- Helical milling
- ±0.01 mm tolerance control (feature-dependent)
Machinable Features for Medical Parts
- Face & shoulder milling
- Dynamic tool paths for complex contours
- O-ring grooves & sealing features
- Counterbores & countersinks
- Chamfers & radius profiles
- Orthopedic slot features
- Precision bore alignment
Burr-Free & Clean Surface Control
- Automated deburring
- Media tumbling
- Brush polishing
- Electro-polishing (for stainless steel)
- Edge-break control
- Particle-free cleaning
Documentation & Validation
- CMM dimensional reports
- First Article Inspection (FAI)
- PPAP if required
- Traceability records
- Surface roughness measurement
- Material certificates
General Tolerance Guideline for Medical Die Casting Parts
Below are typical achievable tolerances (feature-dependent):
| Feature | Tolerance Capability |
|---|---|
| Linear dimension | ±0.05 mm – ±0.10 mm (machined ±0.01 mm) |
| Hole diameter (machined) | ±0.01 – ±0.03 mm |
| Flatness | ≤0.02 – 0.05 mm |
| Roundness | ≤0.01 – 0.03 mm |
| Thread accuracy | 6H / 6g / UNC / UNF / MJ |
| Surface roughness | Ra 0.8 – 1.6 μm (machined) |
Surface Finishing for Medical Components
Surface finishing enhances corrosion resistance, cosmetic quality, ergonomics, and cleanability.
Anodizing (Type II & III)
- Suitable for aluminum housings and handles
- Improves corrosion resistance
- Available in medical grade clear, black, etc.
Electropolishing (Stainless Steel)
- Improves corrosion resistance
- Reduces surface roughness
- Suitable for surgical tools
Liquid Painting & Powder Coating
- RoHS compliant coating systems
- Uniform cosmetic appearance
- Chemical-resistant options for cleaning agents
Passivation
- Applied to stainless steel to remove free iron
- Increases corrosion resistance
Electroless Nickel Plating
- Cosmetic or functional
- Used in hospital hardware and dental equipment
Sandblasting / Bead blasting
- Satin texture for ergonomic surfaces
- Improves coating adhesion
Brushing
- Applied to aluminum housings after machining
- Controls surface roughness and visual uniformity
- Used on visible panels to reduce cosmetic variation
Chromate conversion
- Applied to aluminum die cast components
- Maintains electrical conductivity and grounding
- Used for corrosion protection under RoHS compliance
Laser marking
- Permanent marking on aluminum and zinc parts
- No inks or chemicals, no effect on tolerances
- Supports serial numbers and traceability
Case Studies (Typical Applications)
Below are representative examples showing how engineering collaboration reduces risk and cost.
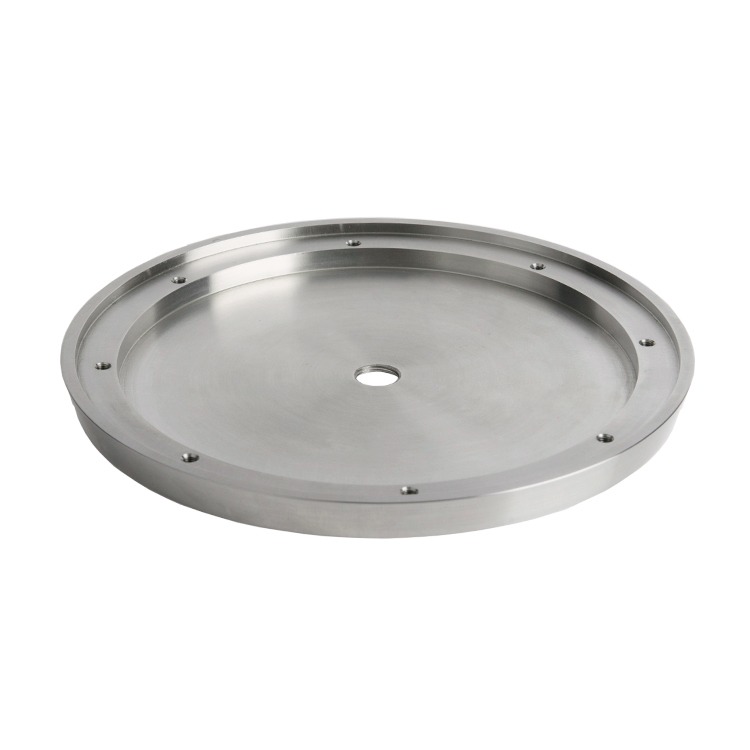

Case A: Ultrasound Housing Weight Reduction
- Objective: Reduce weight for improved portability
- Material: Aluminum alloy
- Method: HPDC + thin-wall optimization
- Result: 22% weight reduction + improved heat dissipation

Case B: Patient Monitor Chassis Alignment
- Objective: Achieve precise alignment for PCB mounting
- Method: Casting + CNC machining on critical features
- Result: ±0.02 mm hole alignment tolerance achieved
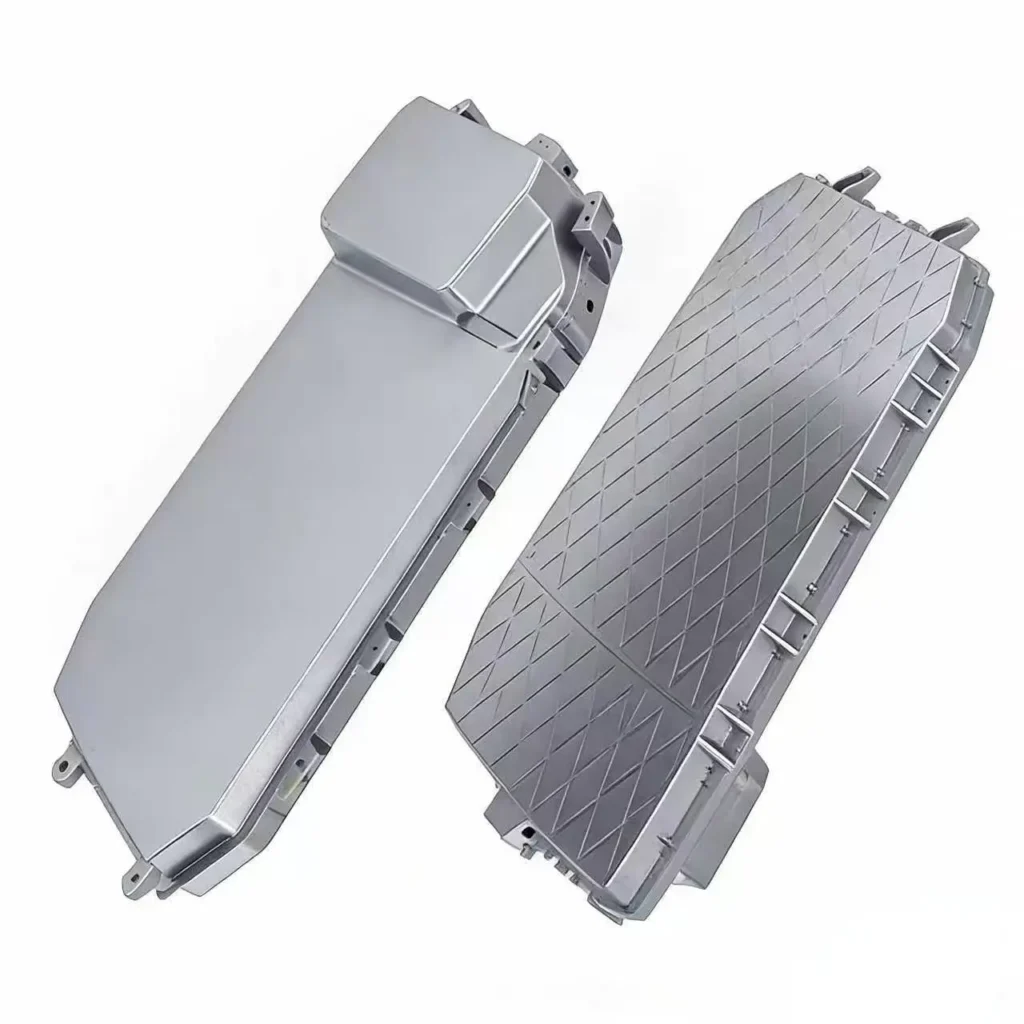

Case C: Dental Imaging Bracket Shielding
- Objective: Provide EMI shielding for digital imaging sensors
- Material: Magnesium alloy
- Finish: Conductive coating
- Outcome: Reduced electronic interference & stable performance
Start Your Medical Device Project
IEC Mould supports medical OEMs from early engineering to mass production. To get started, simply send:
- 2D/3D files
- Estimated annual volumes
- Key requirements
Our team will provide a fast quotation with cost, lead time, and technical feedback.
