High-Performance Die Cast Tooling That Excels in Real Production
- Precision die casting molds for aluminum, zinc, and magnesium
- Long mold life with predictable maintenance and stable yield
- Proven reliability in automotive and industrial programs worldwide
Who We Are — A Die Casting Tooling Manufacturer
We are a China-based die casting tooling and die mold manufacturer, not a trading company or sourcing agent.
All critical processes are handled in-house:
- Tooling engineering and die casting mold design for aluminum, zinc, and magnesium
- CNC machining, EDM, and precision fitting of die casting dies
- Mold assembly, tryout, and validation
- Tool modification, optimization, and maintenance
With ISO 9001 and IATF 16949 certification, our precision die casting tooling systems support automotive and industrial production standards, ensuring consistent quality and traceability.
What We Provide — Complete Die Casting Tooling Services
We provide complete die casting tooling services, covering the full lifecycle. Our goal is not to sell the cheapest casting mold — it is to deliver high-performance die casting tooling solutions that perform predictably in real production conditions.
Die casting mold design

Engineering support

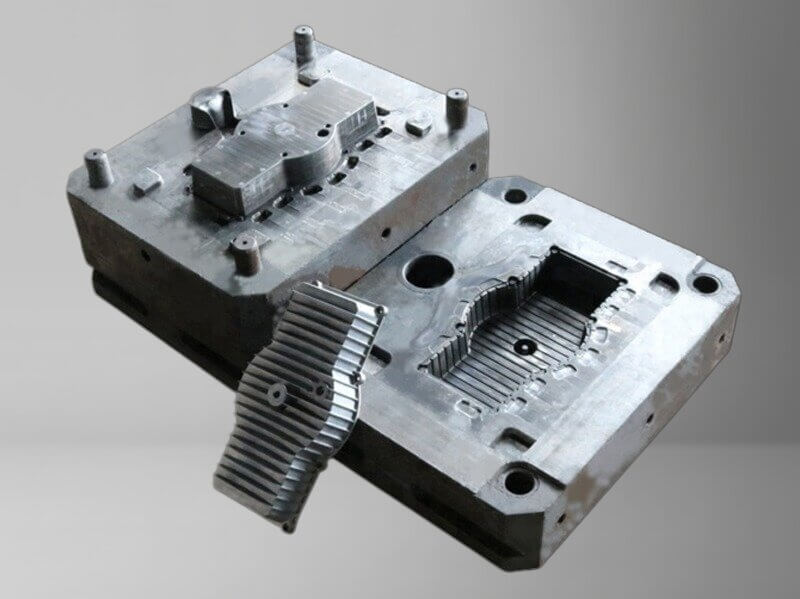
Prototype die casting tooling for early functional validation

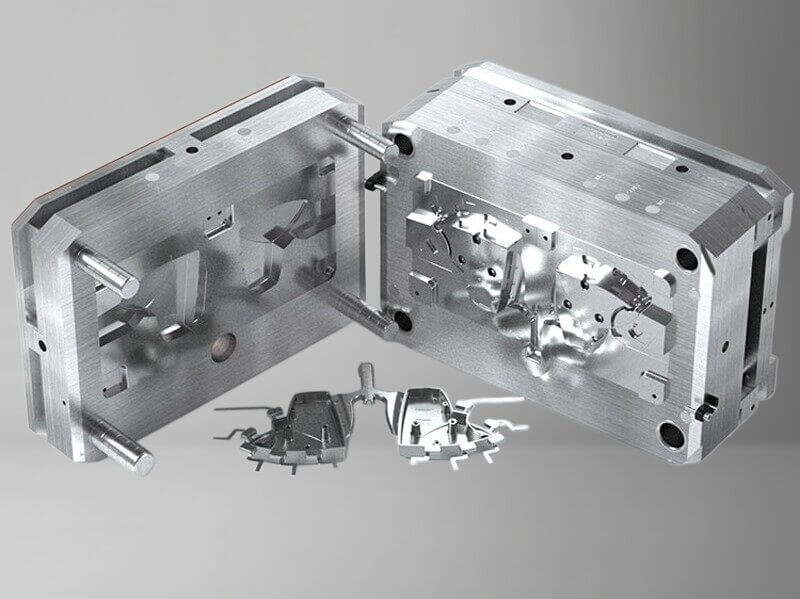
Bridge tooling for low-to-medium volume production

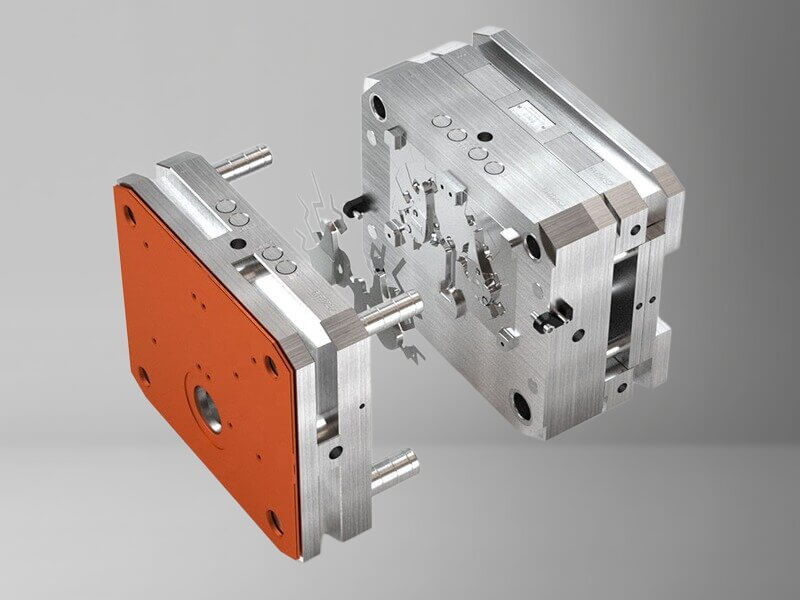
Mass production die casting molds and dies for long-term programs

Tooling modification, optimization, and repair
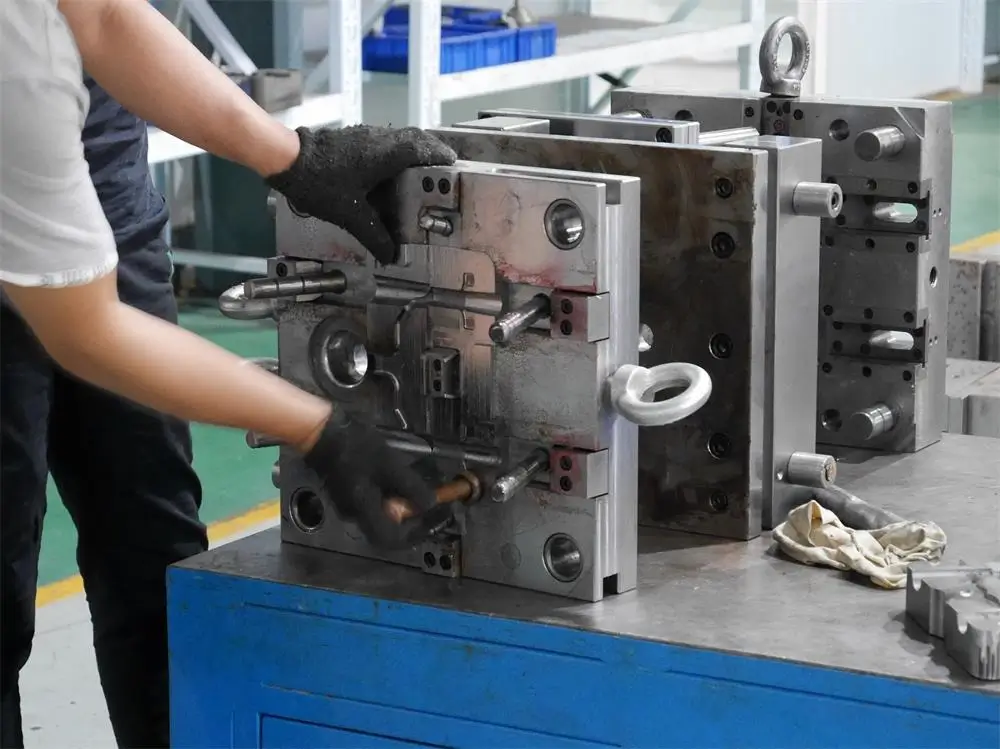

Our Die Casting Tooling Capabilities
We specialize in crafting precision-engineered die tooling for every stage of production, from initial validation to high-volume programs. Every die casting mold and tooling system we create is carefully engineered based on alloy properties, shot volume, thermal behavior, and projected mold life — guaranteeing maximum productivity, minimal maintenance, and long-term cost efficiency.

Aluminum Die Casting Mold
Delivering robust structural and functional components designed for demanding industrial and automotive applications.。
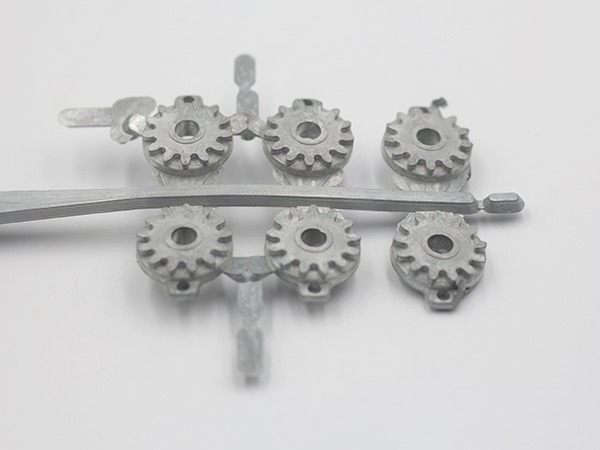

Zinc Die Casting Molds & Dies
Delivering robust structural and functional components designed for demanding industrial and automotive applications.。
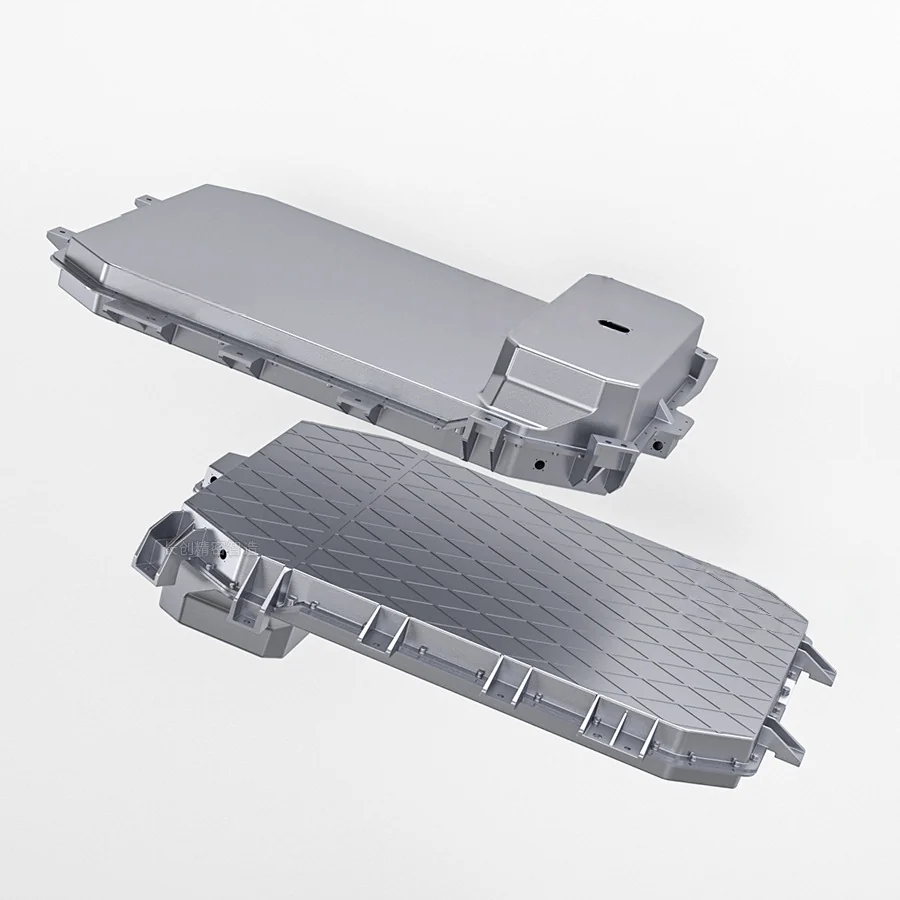

Magnesium Die Casting Tooling
Lightweight, high-strength molds optimized for performance-critical applications.
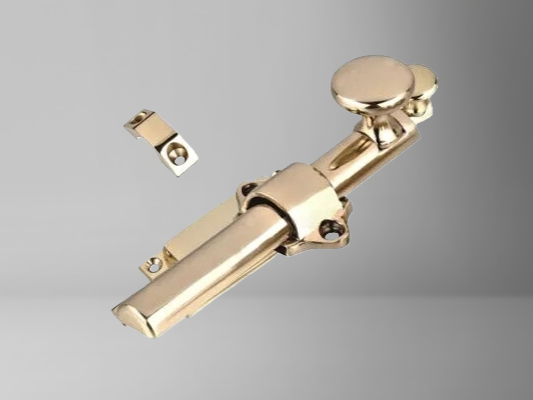

Brass/Copper Die Casting Mold
Designed for components requiring superior electrical conductivity, thermal performance, and corrosion resistance, commonly used in electrical, plumbing, and specialty industrial applications.
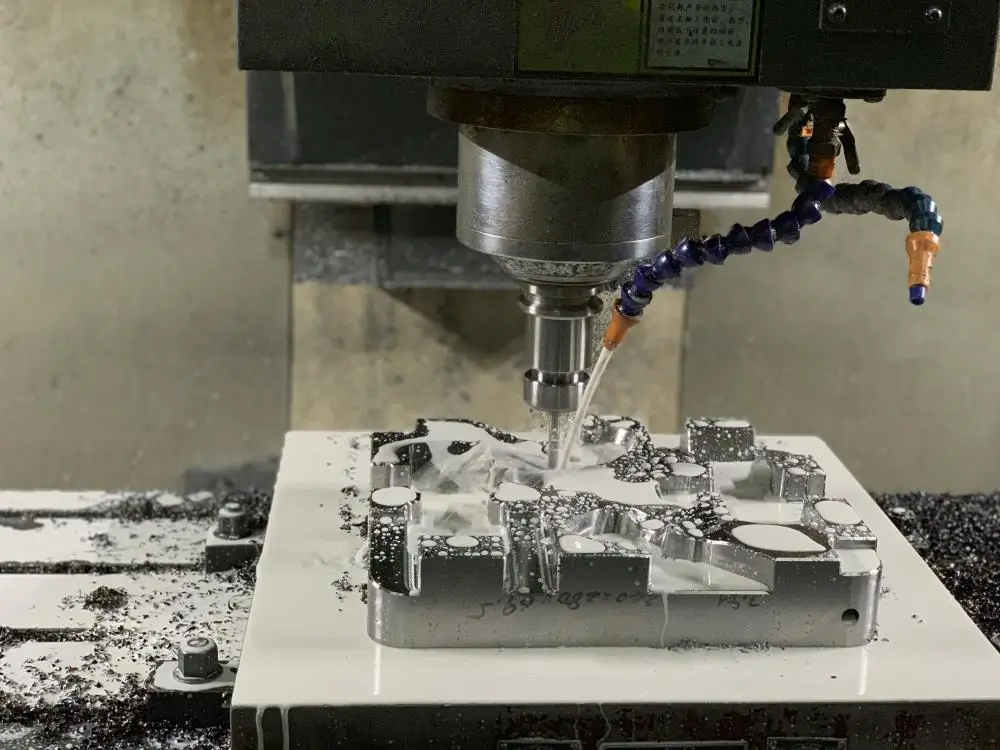

Prototype & Bridge Tooling
Fast, reliable solutions for functional validation and controlled ramp-up before full-scale production.
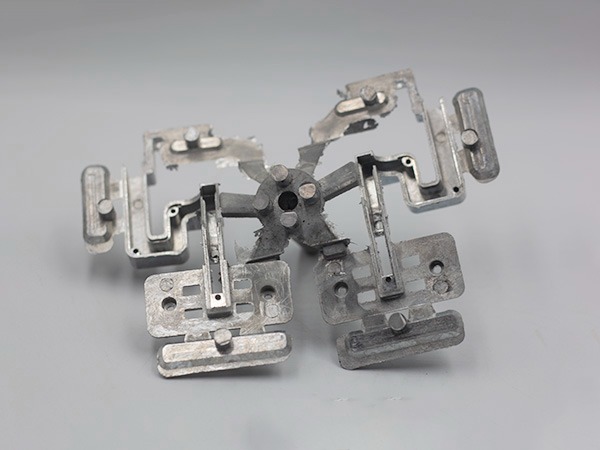

High-Volume Production Die Casting Molds
Engineered for longevity and stable yield, ensuring consistent quality across hundreds of thousands of shots.
Key Engineering Features Built into Our Die Mold
Designed for Production Reality — Not Just Sample Approval. Most die casting tooling looks acceptable during T0 or T1. The real test begins after thousands of shots in continuous production. Our die casting tooling is engineered with one clear objective: to remain stable, predictable, and serviceable long after SOP — when most molds start to fail.
What Makes Our Die Tooling Perform Differently?
- Every die casting mold begins with a rigorous DFM review — not as a formality, but as a risk-elimination process.
- We identify dimensional, thermal, and ejection risks before steel is cut, reducing late-stage changes, delays, and cost overruns.
Metal flow is engineered, not guessed.
Our gating and runner systems are designed to minimize turbulence and air entrapment, while venting and cooling layouts are optimized for balanced solidification — directly reducing porosity, soldering, and scrap in die casting production.
Uniform temperature control prevents thermal shock, reduces distortion, and keeps cycle times consistent across long production runs.
Wear-prone areas are designed for fast replacement—protecting your investment while minimizing downtime and maintenance cost.
Material choice and heat treatment are matched precisely to alloy type, shot volume, and production intensity—extending mold life and maintaining dimensional stability.
In real production environments, well-engineered die casting tooling translates directly into measurable operational advantages, not just better-looking samples. The result is a tooling system that supports production teams rather than creating firefighting situations — delivering a lower total cost of ownership over the life of the program, even when the initial tooling investment is higher.
Consistently lower scrap and rework rates, even as shot counts increase
Significantly less soldering, erosion, and thermal fatigue, extending usable mold life
Predictable and repeatable cycle times, enabling accurate capacity planning
Planned, preventive maintenance instead of costly unplanned downtime
Dimensional stability maintained over long production runs, reducing downstream adjustment and inspection effort
Who This Die Tooling Service Is For?
Our die tooling services are designed for production-focused teams who view tooling as a long-term manufacturing asset, not a one-time purchase. We are typically a strong fit for:
- Design and manufacturing engineers who need tooling that behaves predictably beyond T0/T1 and remains stable after SOP
- Procurement teams responsible for balancing upfront tooling cost with long-term production risk, downtime, and lifecycle cost
- Quality and production managers who prioritize repeatability, stable yield, and controlled maintenance over frequent firefighting
These customers usually operate in environments where tooling performance directly impacts delivery schedules, quality KPIs, and total manufacturing cost. Our tooling services may be less suitable for projects where the primary objective is to minimize initial tooling price at the expense of engineering review, durability, and long-term production stability.

Why Die Casting Mould Fails in Mass Production?
Most die casting tooling does not fail immediately. Problems typically surface after SOP, once the mold is subjected to continuous thermal cycling, high clamping forces, and sustained shot counts — the exact conditions that define real production.
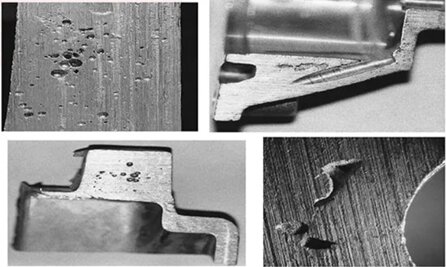
Common failure modes we see in mass production include:
- Thermal imbalance that accelerates heat checking, cracking, and premature fatigue
- Aggressive filling strategies without adequate venting or vacuum support, leading to porosity and instability
- Dimensional drift caused by insufficient rigidity or poorly managed thermal expansion
- Flash and mismatch resulting from weak mold structure or underestimated locking forces
- Maintenance-unfriendly designs that turn routine wear into production-stopping events
These issues are rarely resolved through machine parameter adjustments alone. In nearly every case, they originate from early tooling design decisions — material selection, cooling layout, gating philosophy, and structural assumptions. Mass production performance is not tuned at the machine. It is engineered into the tooling from the very beginning.
What Is Die Casting Tooling?
Die casting tooling is not simply a mold — it is a production control system that governs quality, productivity, and long-term cost. Well-designed tooling directly determines:
Dimensional accuracy and repeatability
Internal soundness and porosity risk
Surface finish and cosmetic consistency
Cycle time stability
Mold life and maintenance frequency
For high-pressure die casting, tooling is the single most critical factor influencing whether a program runs predictably or struggles throughout its lifecycle.

How Die Casting Tooling Works?
In production, die casting tooling operates under continuous thermal and mechanical stress. Every cycle subjects the tooling to:
Rapid temperature change
High injection pressure
Clamping force and mechanical load
Because these stresses repeat tens or hundreds of thousands of times, tooling performance is defined not by initial samples, but by how well the system manages heat, force, and wear over time.
This is why tooling engineering quality has a direct and lasting impact on production stability.
Our Casting Mould Engineering Philosophy
Mass production success is not tuned at the machine — it is engineered into the tooling. We design tooling as a long-term production system, not a short-term deliverable. Our approach is based on real production experience:
- Thermal balance prioritized over maximum fill speed
- Gating designed to minimize turbulence and air entrapment
- Modular inserts for wear areas
Tooling decisions are based on documented failure modes and long-term behavior — not assumptions.
Our Casting Mold Engineering Validation: DFM & Moldflow
This is where tooling risk is either eliminated early or locked in forever. Before any steel is cut, we use DFM review and Moldflow simulation to challenge assumptions, expose weak points, and verify that the tooling concept will survive real production conditions — not just pass a sample run.
DFM Review focuses on production reality:
- Ejection layout, deformation risk, and long-term dimensional control
- Wall thickness balance, draft angles, and tolerance sensitivity
- Parting line definition, slider/lifter feasibility, and wear risk
- Gate location strategy and metal flow direction
Moldflow Simulation evaluates process behavior under load:
- Solidification sequence, hot spots, and thermal imbalance
- Filling pattern, velocity profile, and flow consistency
- Air entrapment risk and venting effectivenes
- Shrinkage tendency and porosity risk
Design optimization happens before die casting mold steel cutting begins, when changes are fast, low-risk, and cost-effective — not after problems appear on the shop floor.
Die Casting Mold Structure & Components
A die casting mold is not a single tool, but a highly integrated mechanical and thermal system. Each component plays a specific role in controlling metal flow, heat transfer, dimensional accuracy, and long-term durability.
A complete die casting tooling system typically includes:
- Fixed and moving die halves engineered for rigidity, alignment accuracy, and clamping force distribution
- Inserts, core pins, sliders, and lifters designed as replaceable wear components to localize maintenance and extend overall mold life
- Ejection systems optimized for balanced force, smooth part release, and minimal deformation
- Cooling circuits strategically placed to manage thermal balance, reduce cycle variation, and limit heat-related fatigue
- Gating, runner, overflow, and venting systems designed to control filling behavior, minimize turbulence, and ensure consistent part quality
Rather than treating these elements independently, we engineer tooling structure as a coordinated system, where mechanical strength, thermal stability, and service accessibility are considered together.
This system-level approach is essential for maintaining dimensional consistency, predictable cycle times, and reliable performance throughout the full production life of the mold
Casting Tool Steel Selection & Heat Treatment
Tool steel selection is not a catalog choice — it is a life-cycle engineering decision that directly affects mold life, thermal fatigue resistance, maintenance frequency, and production stability. We select tool steels based on alloy type, thermal load, expected shot count, and wear behavior, rather than applying a one-grade-fits-all approach. Typical tool steels include:

H13 / 1.2344
Widely used for aluminum HPDC tooling, offering strong resistance to thermal fatigue, cracking, and heat checking under high-temperature cycling
SKD61 / 1.2343
Selected where improved toughness and crack resistance are required, particularly for cores and areas exposed to high mechanical stress

Specialized wear-resistant steels
Applied selectively for inserts, core pins, and gate areas subjected to erosion, soldering, or abrasive wear

Rather than over-hardening the entire mold, we apply targeted material strategies — using different steels or insert designs where wear is concentrated — to extend overall mold life while keeping maintenance efficient. All tooling undergoes controlled heat treatment with documented parameters, followed by:
- Hardness verification
- Microstructure consistency checks
- Stress relief where required
This controlled approach ensures the tooling achieves the required hardness–toughness balance, reducing the risk of premature cracking, deformation, or unpredictable wear during long-term mass production.
Die Casting Die Tooling Manufacturing Process
Our Die Casting Die tooling manufacturing process is structured to protect engineering intent, control risk, and ensure repeatability — not simply to move steel through machines. Each stage is sequenced to prevent downstream correction and preserve long-term performance:
- Engineering approval & design freeze — tooling concept, steel strategy, cooling, and maintenance philosophy locked
- CNC rough machining — material removal with allowance for heat treatment distortion
- Controlled heat treatment — hardness and stress profile established before precision finishing
- CNC finish machining — critical dimensions, shut-offs, and alignment surfaces completed
- EDM & wire cutting — complex features, ribs, gates, and deep cavities produced with accuracy
- Surface preparation & polishing — functional finishes applied based on part and alloy requirements
- Mold assembly — mechanical fit, movement, and safety systems verified
- Internal validation & tryout preparation — tooling verified before entering machine trials
This disciplined process ensures the tooling behaves in production as engineered — not as corrected after the fact.
Die Tooling Tryout & Production Readiness
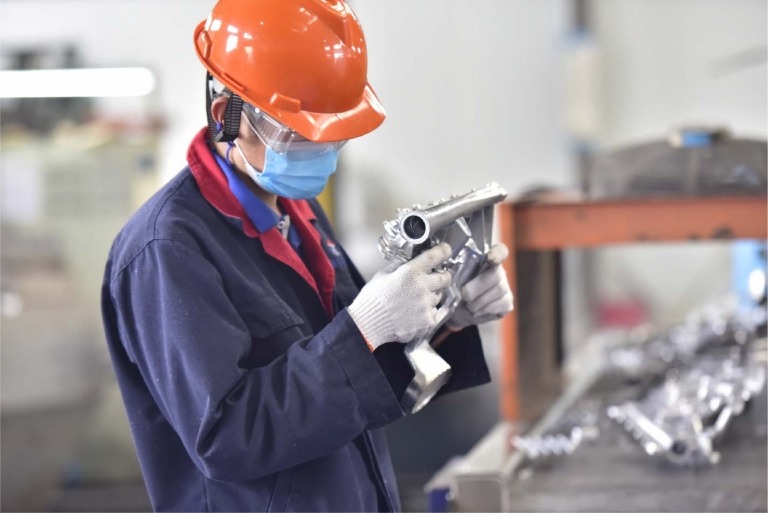

Tooling tryout is not about achieving a cosmetic sample — it is about confirming that the tooling can operate stably, repeatedly, and safely under real production conditions. Our tryout and validation focus on:
- T0 / T1 / T2 trials with controlled parameter windows
- First Article Inspection (FAI) and dimensional stability checks
- Evaluation of filling behavior, venting effectiveness, and thermal balance
- Identification of wear-prone areas before volume production
Sample approval is a milestone. Production readiness means the tooling can run predictably over time, with defined parameters, controlled maintenance points, and no reliance on constant adjustment.
Request a Die Casting Tooling Review
Share your drawing, alloy, and production target. Our engineers will recommend the most suitable die casting tooling strategy — prototype, bridge, or mass production.
